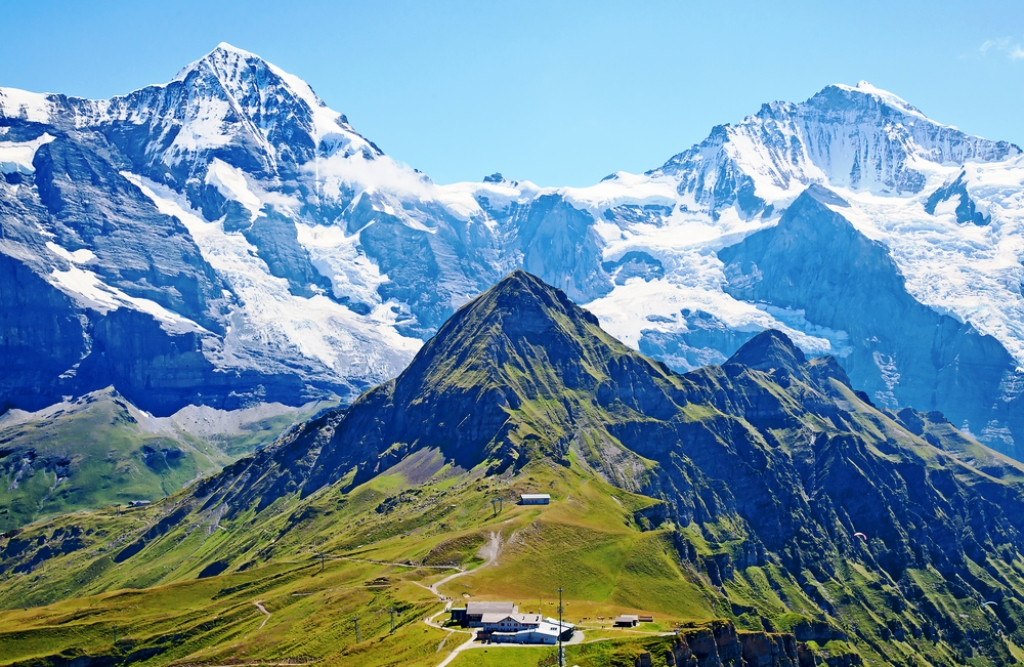
Inclination must be ignored for area to work on a map, plus the inclination ends up being lost in the noise on a large scale. It is very similar to the coastline issue where the more detail you include the longer the coastline gets until every coastline is basically infinite.
Let's take an area split into a grid. One are has a hilly round slope, one is flat, and the rest are a variety of combinations. If you tried to take slope into account the one with the round hill would require the straight lines of the grid to warp towards it like one of those space time curvature pictures. The one that is flat is the only one that could be square, and even then it only works if you count it as flat since even flat ground has a small texture.
So no, they don't take elevation into account for maps because it would be far too difficult to measure.
The surface area can only be calculated with a defined level of accuracy due to how textured surfaces work.