JPEG XL: How It Started, How It’s Going
JPEG XL: How It Started, How It’s Going
Rise of JPEG XL: Apple's Support and Image Compression Insights
JPEG XL: How It Started, How It’s Going

Rise of JPEG XL: Apple's Support and Image Compression Insights

You're viewing a single thread.
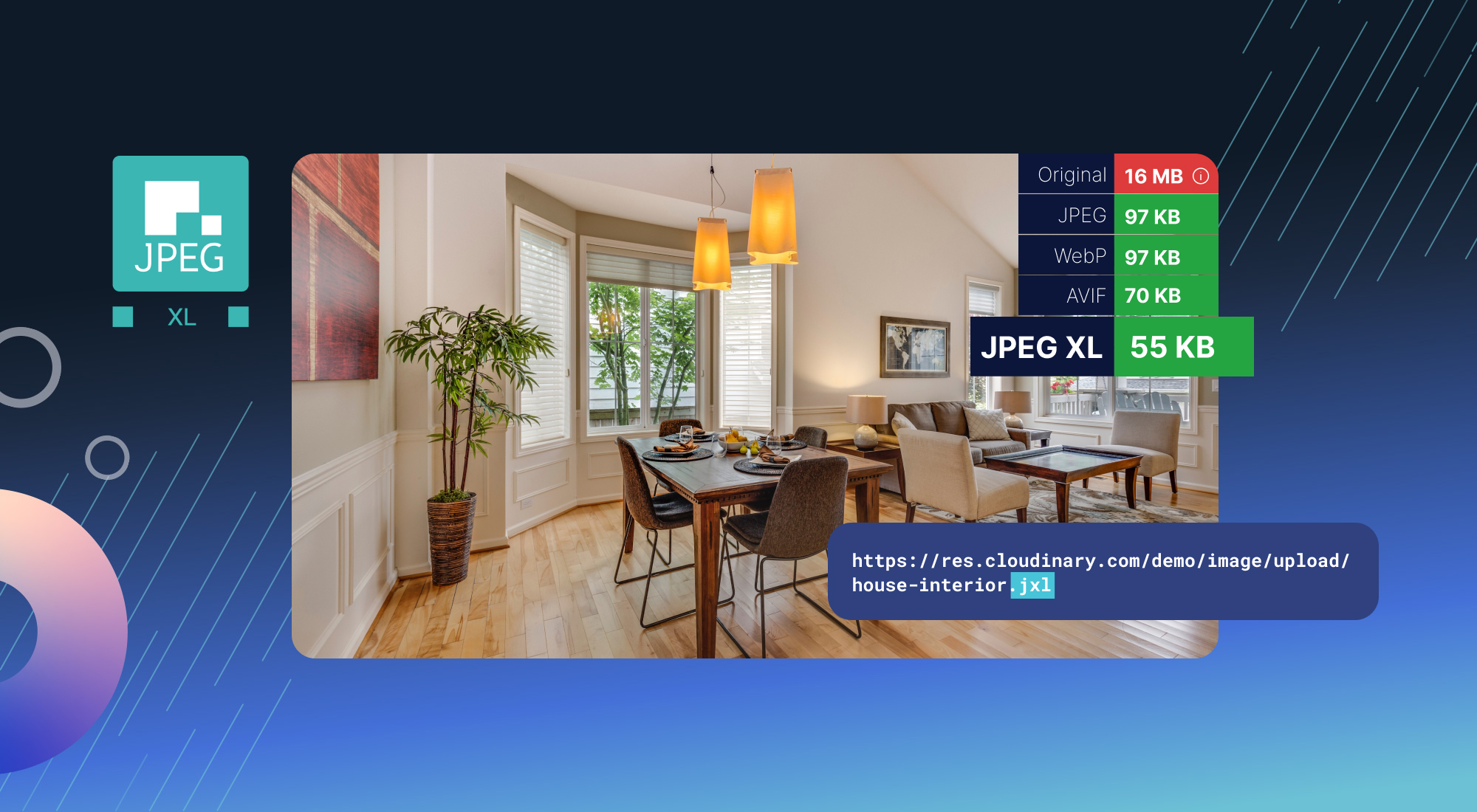
What is the point of this format? How is it any better than png or webp? Do we really need yet another format? I mean 44k really isn’t that great of a savings in the example used.
A shortlist:
If JXL is not the next image format then we will never ever get rid of JPEG and PNG. There has never been a more obviously superior image format in history.
I think you forgot a pretty crucial point, that it is also royalty free. Royalty would be a huge problem.
I have yet to see a general royalty free image format as feature complete and up to date as IFF was for the Amiga back in 1985. From your list, Jpeg XL would finally even surpass that. As a very feature complete format improving on at least 3 formats (GIF PNG JPG)while wrapping them into 1. The only thing missing, is to become universally supported.
I wonder how the Chrome team managed to test it so poorly they claimed it wasn't worth it? Just the versatility alone should make it a no-brainer.
I think you forgot a pretty crucial point, that it is also royalty free.
I'll go back and add it - there's a lot of great stuff that I didn't mention just for brevity. The biggest royalty concern is HEIC atm, which is basically a nonstarter. I'm not sure how the licensing on the other free formats compares against JXL.
I wonder how the Chrome team managed to test it so poorly they claimed it wasn’t worth it? Just the versatility alone should make it a no-brainer.
Make no mistake, it was a political killing. They didn't kill it because of perceived performance, they killed it ahead of their public benchmarks because of "lack of interest". Their cited lack of interest was determined after only a few months of the format going live behind opt-in experimental flags, and once they made their original decision, just about every large tech company spoke up in favor of JXL against Google's decision on their bugtracker, including Adobe, Intel, Nvidia, Facebook, Shopify, and Flickr. Google still plugged their ears and pretended no one was interested.
Google is trying to push WebP (2.0?) and AVIF, and using their browser marketshare to kill JXL and make that happen. Why they went through all this trouble to kill a format that they themselves co-developed, I really have no idea. I follow JXL relatively closely and I still am not 100% sure why they went through with this. All I know is that the decision was politically-motivated, and without applying political/ecosystem pressure they're not going to change their minds with data.
Edit: by the way, the last few comments still trickling in on that bugtracker are a great read, especially #406. #406 reads so similarly to my comment I'm surprised I didn't write it, haha.
Why they went through all this trouble to kill a format that they themselves co-developed, I really have no idea.
I don't know about AVIF, but WebP is a Google format, and they might be doing it for control, like they use control of Chrome to push more advertising.
Google is also a member of the AOM, which created the AV1 format, which AVIF is derivative of - if you're wondering why they're pushing AVIF.
Avif is pushed because it's good and has hardware support across the board
What does google gains by making AVIF win rather than AVIF?
AVIF is derived from the AV1 video codec, which the AOM created, which Google is a part of. The data (basically every single metric), the community, and the websites all favor JXL, and yet Google is intentionally forcing the inferior WebP+AVIF pair against the tide. We can only speculate as to their true reasoning but the most likely answer is that they want their own formats to "win" the next standards race - what benefit that gives them besides ego I truly don't know.
But google also participated to the creation of JPEG-Xl.
And having "their" standard win does not make any sense to me to see where they benefit from it.
As I said earlier and have repeated:
I follow JXL relatively closely and I still am not 100% sure why they went through with this
If you've got a better guess please share. No one knows why they've done it except Google. The popular theory is that they're doing so to push WebP+AVIF instead, because it's one of few ideas that makes sense. We know their decision is political in some nature:
Making one or two of these mistakes before correcting them might be understandable, but making all of them and going radio silent when called out for them means they're doing this with a motive that is not data-driven or in good faith.
This is truly amazing tbh.
ironic this image is in a PNG lol
It's very slow on high compression profiles though, and consumes a lot of resources.
You don't need to use the high compression profiles to get good performance though. If you have a usecase where you are resource limited you should stick to effort levels 5-7 for very little loss in quality, or even 3-4 for lightning quick speed (the default is effort 7). Reference this benchmark against AVIF for effort values vs. speed (SSIMULACRA 2 is a deterministic psychovisual metric - higher is better).
Also, an important consideration in this realm is that JXL makes really clever use of variable-DCT (how big a chunk is) and adaptive quantization (what quality should be used for that chunk), allowing "quality levels" that you specify to be much more visually consistent across every image, instead of other codecs that make some images look bad at quality level 90 and some images look good at level 70. This allows you to select a consistent quality level and lower your encoding effort to compensate, instead of needing to always drive a high quality+effort level to account for every region in a picture looking good.
(If you want a slightly deeper dive into JXL's performance, this is a concise post on various metrics)
I tried getting benefit from the format by recompressing PNGs at some point and it just seemed worthless due to reasons I listed in my comment.
With effort level 7 you should be getting images roughly 2/3's of the size of the original PNG on average (assuming the PNG is already properly optimized). I would try again with at least effort levels 3, 4, 5, and 7. Also consider that PNGs need very expensive CPU time to properly compress them, using a tool like oxipng.
What sort of balance are you looking for with regards to filesize and encode time? At the very least, effort levels 1 through 3 will probably still give you better results than PNG while being ridiculously quick, so there shouldn't be any configuration where PNG is a better choice than JXL with regards to speed.
Graph conveniently omits hardware support, where avif (av1) is supported across the board
No one uses hardware decoding for images - it's just not a good fit for the reality of how we use images. Images are small and easy to decode, whereas starting up a hardware decoder takes a non-trivial amount of time. Additionally, GPU decoders only work single-threaded, so each image would have to be decoded one by one, instead of all at once like with CPU decoding. This was already attempted with VP8/WebP and they gave up trying to make it any good. Videos are good candidates for hardware decoding since they're large and you're only looking at one at a time.
If you have benchmarks or some proof showing otherwise by all means post here.
Funny enough, JXL is supported anywhere you have a general purpose CPU, which is anything consumer with a GUI!
JPEG XL provides comparable image quality to ordinary JPEG compression at around 80% of the file size. It also supports lossless encoding at smaller sizes than PNG, and can handle layers, transparency and CMYK, so in principle it could conveniently replace almost every existing raster image format.
So I agree with your sentiment for the most part. Mainly, it’s frustrating to see all of these new image standards come out which somehow compete with each other due to lack of browser support.
That said 44k isn’t peanuts. That’s a huge reduction, especially on lower end connection speeds.
It is when you’re a cloud hosting platform and you have 1000’s of photos uploaded daily. That 44k saving scales massively when talking about cloud hosting platforms. The jpeg xl format license is more open than webp which is controlled by google.
The new format also enables more features than just file size, a quick google shows it supports animation, 360 photos, and image bursts (as well as more technical specifics that allow for better share ability without needing to have an accompanying json file or dropping to RAW).
This is more important because it means websites can embed photos and the web engine whether it be chromium, Firefox, or safari can handle it natively without needing JavaScript or some other intermediary.
What about png? It’s just another competing standard. At the end of the day it doesn’t really matter, but by not having competing standards we end up having one company controlling it. So since at the very least it gives a decent file size saving it’s good enough for me.
Even better, this must be fantastic when you're training AI models with millions of images. The compression level AND performance should be a game changer.
Hmm, I haven’t delved into image training in a couple years so I’m assuming they still downscale images anyway, so I’m not sure how much the format helps? Do you know if better compression helps at lower resolution? I could see it helping but I could also seeing it be marginal gains and depending on processing time it might not be worth it to convert whole image sets to jpeg xl. And for performance does jpeg xl require less power/time to decode than other formats? Maybe for new image sets going forward it will be the standard.
Oh, I've just been toying around with Stable Diffusion and some general ML tidbits. I was just thinking from a practical point of view. From what I read, it sounds like the files are smaller at the same quality, require the same or less processor load (maybe), are tuned for parallel I/O, can be encoded and decoded faster (and there being less difference in performance between the two), and supports progressive loading. I'm kinda waiting for the catch, but haven't seen any major downsides, besides less optimal performance for very low resolution images.
I don't know how they ingest the image data, but I would assume they'd be constantly building sets, rather than keeping lots of subsets, if just for the space savings of de-duplication.
(I kinda ramble below, but you'll get the idea.)
Mixing and matching the speed/efficiency and storage improvement could mean a whole bunch of improvements. I/O is always an annoyance in any large set analysis. With JPEG XL, there's less storage needed (duh), more images in RAM at once, faster transfer to and from disc, fewer cycles wasted on waiting for I/O in general, the ability to store more intermediate datasets and more descriptive models, easier to archive the raw photo sets (which might be a big deal with all the legal issues popping up), etc. You want to cram a lot of data into memory, since the GPU will be performing lots of operations in parallel. Accessing the I/O bus must be one of the larger time sinks and CPU load becomes a concern just for moving data around.
I also wonder if the support for progressive loading might be useful for more efficient, low resolution variants of high resolution models. Just store one set of high res images and load them in progressive steps to make smaller data sets. Like, say you have a bunch of 8k images, but you only want to make a website banner based on the model from those 8k res images. I wonder if it's possible to use the the progressive loading support to halt reading in the images at 1k. Lower resolution = less model data = smaller datasets to store or transfer. Basically skipping the downsampling.
Any time I see a big feature jump, like better file size, I assume the trade off in another feature negates at least half the benefit. It's pretty rare, from what I've seen, to have improvements on all fronts.
JXL has been ready for practical use for a while now - the only place where JXL support is still missing is browsers (due to Google's politically-motivated removal from chromium). I'm not sure if anyone has tried using JXL with ML, but it's certainly ready to be tested right now. IMO JXL has been ready since their libJXL 0.7.0 release, which happened September 2022 last year. They're still working towards a 1.0 but every image-related application has built-in support for JXL already and it can more or less be considered ready.
haven’t seen any major downsides, besides less optimal performance for very low resolution images
Just to note here, to be precise AVIF starts (barely) winning at low fidelity ranges, not low resolution. Meaning if you want a blurry mess that looks like this, AVIF will compress slightly better (that's an actual AVIF converted to PNG by the way).
At the risk of sounding like sour grapes, this compression advantage doesn't truly matter. This level of compression is almost never used, and even if it was, even drastic relative filesize savings would ultimately amount to bytes/kilobytes in the grand scheme of all images you're serving. It's more impactful to compress large images simply because they are larger. Smaller images are already small and efficiency deltas in a 1kB vs 1.1kB image are meaningless compared to a 600kB vs 800kB image.
I also wonder if the support for progressive loading might be useful for more efficient, low resolution variants of high resolution models. Just store one set of high res images and load them in progressive steps to make smaller data sets. Like, say you have a bunch of 8k images, but you only want to make a website banner based on the model from those 8k res images. I wonder if it’s possible to use the the progressive loading support to halt reading in the images at 1k
I'm not fully confident on this aspect but I'm pretty sure that JXL supports more than just traditional progressive decoding - you can actually pull "complete" images out of the bitstream from arbitrary ranges. Meaning you could efficiently store a full range of quality options in just one image, then serve them on the fly.
Any time I see a big feature jump, like better file size, I assume the trade off in another feature negates at least half the benefit. It’s pretty rare, from what I’ve seen, to have improvements on all fronts.
JXL is self-described "alien technology from the future", and it was made by a "dream team" of image engineers who have had a hand in just about every image codec and compression technique from our past. It also benefits from being a real image codec, whereas every recent image format that has gained widespread adoption has been derived from a video codec (WebP, AVIF, HEIC).
The only truly useful thing it doesn't perform best-in-class at is animation encoding (losing to AVIF because it's based on the amazing AV1 video codec), and I would honestly recommend just serving AV1 videos instead, and skipping image formats entirely.
A neutral aspect of JXL is that it does worse in single-core decode speed compared to JPEG (which is disgustingly fast), but JXL can be parallelized whereas JPEG cannot. This is ultimately an advantage for JXL for general usecase where users have at least 4 cores available, but for large-scale distributed processing I imagine this property of JPEG may still have an edge use-case?
If you're curious about the technical aspects of JXL, I recommend reading their official slidedeck. The nitty-gritty details start at page 59, but the whole thing is a good read.
At first glance, I probably thought JXL was another attempt at JPEG2000 by a few bitter devs, so I had ignored it.
Yeah, my examples/description was more intended to be conceptual for folks that may not have dealt with the nitty gritty. Just mental exercises. I've only done a small bit of image analysis, so I have a general understanding of what's possible, but I'm sure there are folks here (like you) that can waaay outclass me on details.
These intermediate-to-deep dives are very interesting. Not usually my cup of tea, but this does seem big. Thanks for the info.
Interesting I hadn’t thought about how the reduced image size could allow for more data throughput overall. Also great to hear that’s it’s similar or lower processing required. Although I’m not sure what tuned for parallel I/O means? Do they split the data into subgroups so multiple threads can process it at the same time?
(fair warning - I go a little overboard on the examples. Sorry for the length.)
No idea on the details, but apparently it's more efficient for multithreaded reading/writing.
I guess that you could have a few threads reading the file data at once into memory. While one CPU core reads the first 50% of the file, and second can be reading in the second 50% (though I'm sure it's not actually like that, but as a general example). Image compression usually works some form of averaging over an area, so figuring out ways to chop the area up, such that those patches can load cleanly without data from the adjoining patches is probably tricky.
I found this semi-visual explanation with a quick google. The image in 3.4 is kinda what I'm talking about. In the end you need equally sized pixels, but during compression, you're kinda stretching out the values and/or mapping of values to pixels.
Not an actual example, but highlights some of the problems when trying to do simultaneous operations...
Instead of pixels 1, 2, 3, 4 being colors 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, you apply a function that assigns the colors 1.1, 1.25, 1.25, 1.4. You now only need to store the values 1.1, 1.25, 1.4 (along with location). A 25% reduction in color data. If you wanted to cut that sequence in half for 2 CPUs with separate memory blocks to read at once, you lose some of that optimization. Now CPU1 and CPU2 need color 1.25, so it's duplicated. Not a big deal in this example, but these bundles of values can span many pixels and intersect with other bundles (like color channels - blue can be most efficiently read in 3 pixels wide chunks, green 2 pixel wide chunks, and red 10 pixel wide chunks). Now where do you chop those pixels up for the two CPUs? Well, we can use our "average 2 middle values in 4 pixel blocks" approach, but we're leaving a lot of performance on the table with empty or useless values. So, we can treat each of those basic color values as independent layers.
But, now that we don't care how they line up, how do we display a partially downloaded image? The easiest way is to not show anything until the full image is loaded. Nothing nothing nothing Tada!
Or we can say we'll wait at the end of every horizontal line for the values to fill in, display that line, then start processing the next. This is the old waiting for the picture to slowly load in 1 line at a time cliche. Makes sense from a human interpretation perspective.
But, what if we take 2D chunks and progressively fill in sub-chunks? If every pixel is a different color, it doesn't help, but what about a landscape photo?
First values in the file: Top half is blue, bottom green. 2 operations and you can display that. The next values divide the halves in half each. If it's a perfect blue sky (ignoring the horizon line), you're done and the user can see the result immediately. The bottom half will have its values refined as more data is read, and after a few cycles the user will be able to see that there's a (currently pixelated) stream right up the middle and some brownish plant on the right, etc. That's the image loading in blurry and appearing to focus in cliche.
All that is to say, if we can do that 2D chunk method for an 8k image, maybe we don't need to wait until the 8k resolution is loaded if we need smaller images for a set. Maybe we can stop reading the file once we have a 1024x1024 pixel grid. We can have 1 high res image of a stoplight, but treat is as any resolution less than the native high res, thanks to the progressive loading.
So, like I said, this is a general example of the types of conditions and compromises. In reality, almost no one deals with the files on this level. A few smart folks write libraries to handle the basic functions and everyone else just calls those libraries in their paint, or whatever, program.
Oh, that was long. Um, sorry? haha. Hope that made sense!
Yeah a bit confusing at times but overall very cool and informative, thanks so much!
The article discusses how it's better than webp. Specifically, it's much better at both compression ratios and performance, at all quality levels. WebP has problems where the compression falls off due to being locked to yuv420